鞍山做网站比较好的公司网络暴力事件
一、基本概念
1.1 概念
线程池(Thread Pool)是一种基于池化技术管理线程的机制,旨在减少线程创建和销毁的开销,提高系统资源的利用率,以及更好地控制系统中同时运行的线程数量。线程池通过预先创建一定数量的线程,并将这些线程放入一个“池”中,当有新任务到来时,不是立即创建新线程来执行,而是从线程池中取出一个空闲的线程来执行该任务。如果所有线程都在忙碌,则新任务会等待直到有线程变得空闲。
在C语言中,由于标准库(如C89/C99/C11等)不支持线程或线程池,因此通常需要使用第三方库如POSIX线程(pthread)来实现线程池。
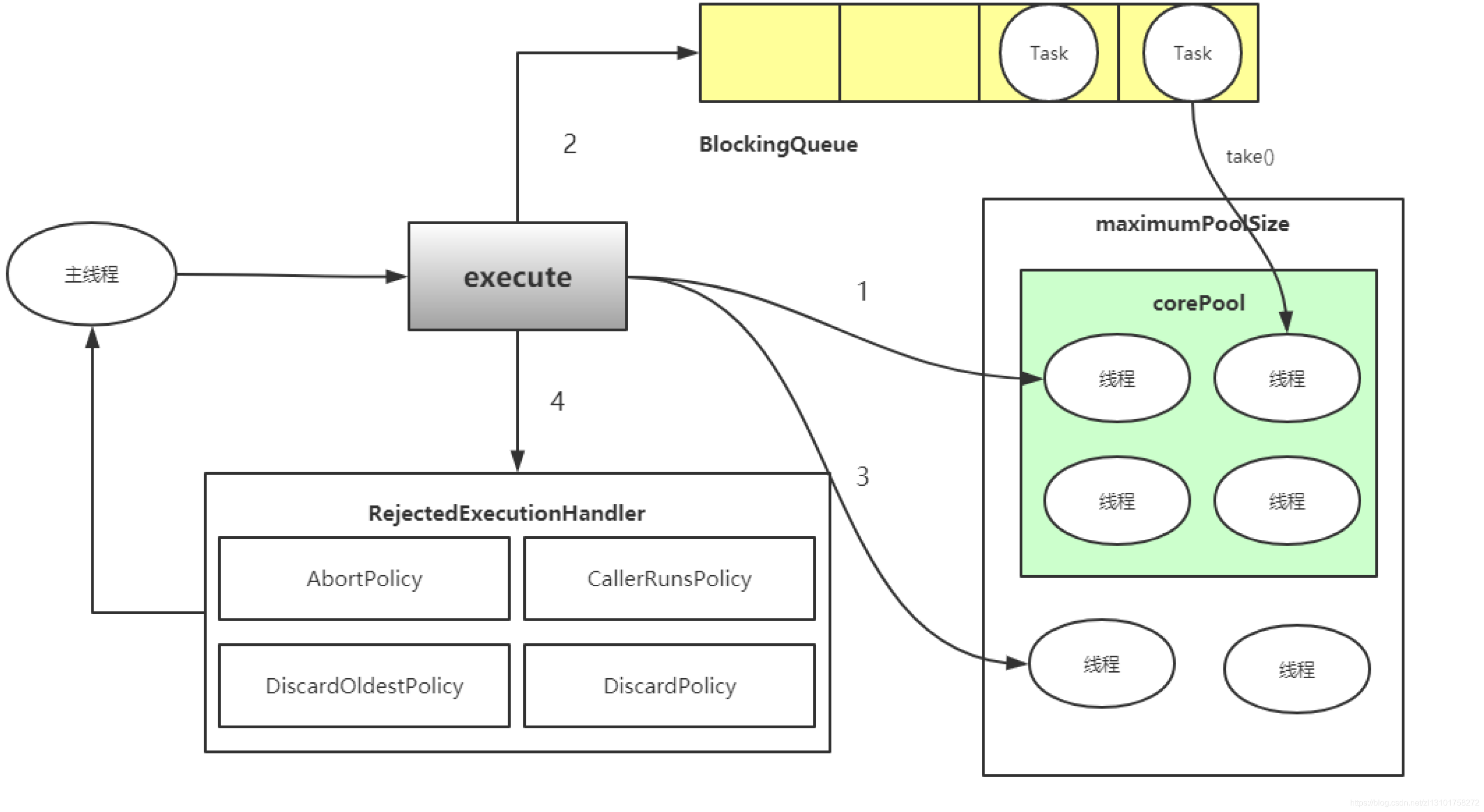
1.2 应用场景【C语言】
C语言中的线程池应用场景与在其他编程语言中类似,主要包括以下几类:
-
高并发服务器: 在网络服务器中处理大量客户端请求。每个请求可以分配给一个线程池中的线程进行处理,以提高响应速度和吞吐量。
-
数据处理和计算密集型任务: 当需要处理大量数据或执行复杂的计算时,可以将任务分配到线程池中并行执行,以缩短总体执行时间。
-
资源密集型任务: 对于需要频繁访问共享资源(如数据库、文件系统等)的任务,使用线程池可以减少线程创建和销毁的开销,并可能通过更高效的资源管理来提高性能。
-
异步操作: 在需要执行非阻塞操作(如异步I/O、异步网络请求等)时,线程池可以用来处理这些异步操作的结果或回调。
-
定时任务和周期性任务: C语言本身不直接支持定时器和周期性任务,但你可以使用线程池中的线程来模拟这些功能,通过轮询或睡眠机制来检查时间并执行相应的任务。
1.3 实现线程池步骤
-
定义线程池结构: 包括线程数量、任务队列、互斥锁、条件变量等;
-
实现任务队列: 用于存储待执行的任务;
-
编写线程工作函数: 该函数将被多个线程同时执行,并从任务队列中取出任务进行处理;
-
初始化和管理线程池: 包括创建线程、启动线程、销毁线程等操作;
-
添加任务到线程池: 提供接口将新任务添加到任务队列中,并通知等待的线程。
由于C语言相对底层,因此实现这些功能需要更多的手动编码和对系统资源的管理。此外,你还需要考虑线程安全和性能优化等问题,第三方库可在C++、python中查找,避免从头实现线程池。
下文将具体说明C语言实现线程池的代码。
二、实现
2.1 定义线程池结构
首先,定义一个包含线程池所需所有信息的结构体,如线程数组、任务队列、互斥锁、条件变量等。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define MAX_THREADS 4 // 任务队列节点
typedef struct task { void (*function)(void*); void* arg; struct task* next;
} task_t; // 线程池结构体
typedef struct { pthread_t threads[MAX_THREADS]; // 线程数组 pthread_mutex_t queue_mutex; // 保护任务队列的互斥锁 pthread_cond_t queue_cond; // 任务队列的条件变量 bool stop; // 线程池停止标志 task_t* head; // 任务队列头指针 task_t* tail; // 任务队列尾指针 int thread_count; // 当前活跃线程数 int active_threads; // 最大活跃线程数(可配置)
} threadpool_t;
2.2 初始化线程池
实现一个函数来初始化线程池,包括创建线程、初始化同步等。
void* worker(void* arg) { threadpool_t* pool = (threadpool_t*)arg; while (true) { pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->queue_mutex); // 如果线程池已停止且没有任务,则退出循环 if (pool->stop && pool->head == NULL) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex); break; } // 等待任务或线程池停止信号 while (!pool->stop && pool->head == NULL && pool->thread_count >= pool->active_threads) { pthread_cond_wait(&pool->queue_cond, &pool->queue_mutex); } // 取出任务(如果线程池未停止且队列不为空) task_t* task = NULL; if (!pool->stop && pool->head != NULL) { task = pool->head; pool->head = task->next; if (pool->head == NULL) { pool->tail = NULL; } pool->thread_count--; } pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex); // 执行任务(如果任务不为空) if (task != NULL) { (*(task->function))(task->arg); free(task); // 释放任务节点内存(如果任务节点是动态分配的) } } return NULL;
} void threadpool_init(threadpool_t* pool, int active_threads) { pool->stop = false; pool->head = pool->tail = NULL; pool->thread_count = 0; pool->active_threads = active_threads; pthread_mutex_init(&pool->queue_mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&pool->queue_cond, NULL); for (int i = 0; i < active_threads; i++) { pthread_create(&pool->threads[i], NULL, worker, pool); }
}
2.3 添加任务到线程池
实现一个函数来向线程池的任务队列中添加任务,并唤醒一个等待的线程(如果有的话)。
void threadpool_add_task(threadpool_t* pool, void (*function)(void*), void* arg) { task_t* new_task = (task_t*)malloc(sizeof(task_t)); new_task->function = function; new_task->arg = arg; new_task->next = NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->queue_mutex); if (pool->tail == NULL) { pool->head = pool->tail = new_task; } else { pool->tail->next = new_task; pool->tail = new_task; } pthread_cond_signal(&pool->queue_cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex);
}
2.4 销毁线程池
实现一个函数来停止所有线程并销毁线程池。
void threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t* pool) { pool->stop = true; pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->queue_cond); for (int i = 0; i < MAX_THREADS; i++) { pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL); } pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->queue_mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->queue_cond);
}
三、完整简单示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>#define MAX_THREADS 5typedef struct task {void (*function)(void*);void* arg;struct task* next;
} task_t;typedef struct {pthread_t threads[MAX_THREADS];pthread_mutex_t queue_mutex;pthread_cond_t queue_cond;bool stop;task_t* head;task_t* tail;int thread_count;int active_threads;
} threadpool_t;void* worker(void* arg) {threadpool_t* pool = (threadpool_t*)arg;while (true) {pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->queue_mutex);while (pool->head == NULL && !pool->stop) {pthread_cond_wait(&pool->queue_cond, &pool->queue_mutex);}if (pool->stop && pool->head == NULL) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex);break;}task_t* task = pool->head;if (task != NULL) {pool->head = task->next;if (pool->head == NULL) {pool->tail = NULL;}}pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex);if (task != NULL) {(*(task->function))(task->arg);free(task); // 释放任务节点内存}sleep(1);}return NULL;
}void threadpool_init(threadpool_t* pool, int active_threads) {pool->stop = false;pool->head = pool->tail = NULL;pool->thread_count = 0;pool->active_threads = active_threads;pthread_mutex_init(&pool->queue_mutex, NULL);pthread_cond_init(&pool->queue_cond, NULL);for (int i = 0; i < active_threads; ++i) {pthread_create(&pool->threads[i], NULL, worker, pool);}
}void threadpool_add_task(threadpool_t* pool, void (*function)(void*), void* arg) {task_t* new_task = (task_t*)malloc(sizeof(task_t));new_task->function = function;new_task->arg = arg;new_task->next = NULL;pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->queue_mutex);if (pool->tail == NULL) {pool->head = pool->tail = new_task;} else {pool->tail->next = new_task;pool->tail = new_task;}pthread_cond_signal(&pool->queue_cond);pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex);
}void threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t* pool) {pool->stop = true;pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->queue_mutex);pthread_cond_broadcast(&pool->queue_cond);pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->queue_mutex);for (int i = 0; i < pool->active_threads; ++i) {pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL);printf("%d\r\n", i);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->queue_mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->queue_cond);
}// 示例任务函数
void example_task(void* arg) {int task_id = *(int*)arg;printf("Task %d is executing\n", task_id);free(arg); // 释放参数内存sleep(1); // 模拟任务执行时间
}int main() {threadpool_t pool;threadpool_init(&pool, 2); // 初始化线程池,最大活跃线程数为2// 添加示例任务for (int i = 0; i < MAX_THREADS; ++i) {int* arg = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));*arg = i;threadpool_add_task(&pool, example_task, arg);}// 等待一段时间,观察任务执行情况sleep(5);// 销毁线程池threadpool_destroy(&pool);return 0;
}
运行结果为:

这段代码演示了一个简单的线程池的使用方式。在主函数中,我们初始化了一个线程池(最大活跃线程数为2),然后添加了5个示例任务(每个任务执行时间模拟为1秒)。在任务执行完毕后,通过调用 threadpool_destroy 函数来销毁线程池,确保所有任务都被执行完毕。
注意:这里销毁的时候保证知道数组中有多少个有效的线程ID,进而销毁。
可在结构体中添加pool->num_threads ,即用来保存线程池中线程数量的成员变量,应该在初始化线程池时进行设置,并在后续操作中根据需要使用,则不会出现在销毁时越界或死锁。
这个示例展示了如何使用线程池来管理并发执行的任务,以及如何通过互斥锁和条件变量来实现线程安全的任务队列操作。
