青岛网站推网上推广app怎么做
文章目录
- 数据代理
- 示例
- 初始化组件实例
- 计算属性
- 基本用法
- ComputedReflmpl类
- 计算属性的创建
- Vue3的特点及优势
- 声明式框架
- 采用虚拟DOM
- 区分编译时和进行时
- Vue3设计思想
数据代理
示例
以下代码主要是有一个msg的响应式数据,点击按钮后修改msg的内容。根据代码可知有两处都存在msg,那么,界面显示的内容是什么?点击按钮修改的又是哪一部分数据?
<template><p>{{ msg }}</p><button @click="changeMsg">点击试试</button>
</template>
<script>import { ref } from 'vue'export default {data() {return {msg: 'msg from data'}},setup() {const msg = ref('msg from setup')return {msg}},methods: {changeMsg() {this.msg = 'change'}}}
</script>
初始化组件实例
setCompontent在源码中的实现
export function setupComponent(instance, isSSR = false) {const { props, children } = instance.vnode// 判断组件是否是有状态的组件const isStateful = isStatefulComponent(instance)// 初始化 propsinitProps(instance, props, isStateful, isSSR)// 初始化 slotsinitSlots(instance, children)// 如果是有状态组件,那么去设置有状态组件实例const setupResult = isStateful? setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR): undefinedreturn setupResult
}在以上setComponent中,组件渲染之后设置组件的状态,通过 isStatefulComponent(instance) 判断是否是有状态的组件,initProps 初始化 props;initSlots 初始化 slots;
根据组件是否是有状态的,来决定是否需要执行 setupStatefulComponent 函数。
判断是否有状态的组件的函数
function isStatefulComponent(instance) {return instance.vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
}setupStatefulComponent函数
setupStatefulComponent就是设置有状态组件,对于有状态组件,Vue内部会保留组件状态数据
function setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR) {// 定义 Component 变量const Component = instance.type// 1. 创建渲染代理的属性访问缓存instance.accessCache = Object.create(null)// 2. 创建渲染上下文代理, proxy 对象其实是代理了 instance.ctx 对象instance.proxy = new Proxy(instance.ctx, PublicInstanceProxyHandlers);// 3. 执行 setup 函数const { setup } = Componentif (setup) {// 如果 setup 函数带参数,则创建一个 setupContextconst setupContext = (instance.setupContext =setup.length > 1 ? createSetupContext(instance) : null)// 执行 setup 函数,获取结果const setupResult = callWithErrorHandling(setup, instance, 0, [instance.props, setupContext])// 处理 setup 执行结果handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult)} else {// 4. 完成组件实例设置finishComponentSetup(instance, isSSR)}
}计算属性
基于响应式依赖进行缓存,并仅在依赖项变化时重新计算。
基本用法
import {reactive,computed} form "vue";
const state = reactive({count:1,
});
const plusOne = computed(()=>state.count+1);
console.log(plusOne.value) //2
state.count++;
console.log(plusOne.value) //3
ComputedReflmpl类
export class ComputedRefImpl<T> {//用于存储与此计算属性相关的依赖(副作用函数)。public dep?: Dep = undefined//用于存储计算属性的当前值private _value!: T//一个 ReactiveEffect 实例,用于封装计算属性的 getter 函数。//这个副作用函数会在依赖的响应式数据变化时重新执行,以更新计算属性的值public readonly effect: ReactiveEffect<T>//内部标志,用于标记这个对象是一个 Ref 类型,并且指示其只读状态。public readonly __v_isRef = truepublic readonly [ReactiveFlags.IS_READONLY]: boolean = falsepublic _cacheable: boolean/*** Dev only*/_warnRecursive?: boolean/*** 构造函数接收四个参数:* getter: 用户定义的计算属性的获取函数。* _setter: 用户定义的计算属性的设置函数,用于允许计算属性被赋新值。* isReadonly: 表明这个计算属性是否是只读的。* isSSR: 标记是否在服务器端渲染环境中使用,影响是否缓存计算结果。*/constructor(private getter: ComputedGetter<T>,private readonly _setter: ComputedSetter<T>,isReadonly: boolean,isSSR: boolean,) {//ReactiveEffect 被用于封装 getter 函数,确保每当依赖的数据变化时,都能够自动重新计算值,并缓存结果以提高性能。this.effect = new ReactiveEffect(() => getter(this._value),() =>triggerRefValue(this,this.effect._dirtyLevel === DirtyLevels.MaybeDirty_ComputedSideEffect? DirtyLevels.MaybeDirty_ComputedSideEffect: DirtyLevels.MaybeDirty,),)this.effect.computed = thisthis.effect.active = this._cacheable = !isSSRthis[ReactiveFlags.IS_READONLY] = isReadonly}/*** 当访问计算属性的 value 时,会执行这个 getter 函数。* 这个函数首先检查是否需要重新计算计算属性的值(基于缓存逻辑和依赖数据的变化)。* 如果需要,它会运行封装的 getter 函数来更新 _value。* 然后,它会注册当前活动的副作用函数为这个计算属性的依赖,以便将来数据变化时能触发更新*/get value() {// the computed ref may get wrapped by other proxies e.g. readonly() #3376//“获取当前计算属性实例(this)背后的原始对象,并将其赋值给 self 变量”const self = toRaw(this)if ((!self._cacheable || self.effect.dirty) &&hasChanged(self._value, (self._value = self.effect.run()!))) {triggerRefValue(self, DirtyLevels.Dirty)}trackRefValue(self)if (self.effect._dirtyLevel >= DirtyLevels.MaybeDirty_ComputedSideEffect) {if (__DEV__ && (__TEST__ || this._warnRecursive)) {warn(COMPUTED_SIDE_EFFECT_WARN, `\n\ngetter: `, this.getter)}triggerRefValue(self, DirtyLevels.MaybeDirty_ComputedSideEffect)}return self._value}set value(newValue: T) {this._setter(newValue)}// #region polyfill _dirty for backward compatibility third party code for Vue <= 3.3.xget _dirty() {return this.effect.dirty}set _dirty(v) {this.effect.dirty = v}// #endregion
}这个类通过 ReactiveEffect 封装 getter 函数,使计算属性能够响应依赖数据的变化。同时,通过缓存机制保证了性能的优化。
计算属性的创建
/*** 接受一个 getter 函数作为参数。这个 getter 函数定义了计算属性的计算逻辑,* 当依赖的响应式数据变化时,这个函数会被重新执行来更新计算属性的值。* 在这种情况下,计算属性是只读的,尝试写入会导致警告(在开发模式下)。*/
export function computed<T>(getter: ComputedGetter<T>,debugOptions?: DebuggerOptions,
): ComputedRef<T>/*** 接受一个包含 get 和 set 方法的对象 options 作为参数* 这允许你创建一个可写的计算属性。get 方法定义了计算逻辑,和只读计算属性一样。* set 方法允许你自定义当尝试修改计算属性的值时的行为,这在需要基于计算属性的值反向更新其依赖的响应式数据时非常有用。*/
export function computed<T>(options: WritableComputedOptions<T>,debugOptions?: DebuggerOptions,
): WritableComputedRef<T>export function computed<T>(getterOrOptions: ComputedGetter<T> | WritableComputedOptions<T>,debugOptions?: DebuggerOptions,isSSR = false,
) {let getter: ComputedGetter<T>let setter: ComputedSetter<T>const onlyGetter = isFunction(getterOrOptions)if (onlyGetter) {getter = getterOrOptionssetter = __DEV__? () => {warn('Write operation failed: computed value is readonly')}: NOOP} else {getter = getterOrOptions.getsetter = getterOrOptions.set}//使用 ComputedRefImpl 类来实际创建计算属性const cRef = new ComputedRefImpl(getter, setter, onlyGetter || !setter, isSSR)if (__DEV__ && debugOptions && !isSSR) {cRef.effect.onTrack = debugOptions.onTrackcRef.effect.onTrigger = debugOptions.onTrigger}return cRef as any
}
Vue3的特点及优势
声明式框架
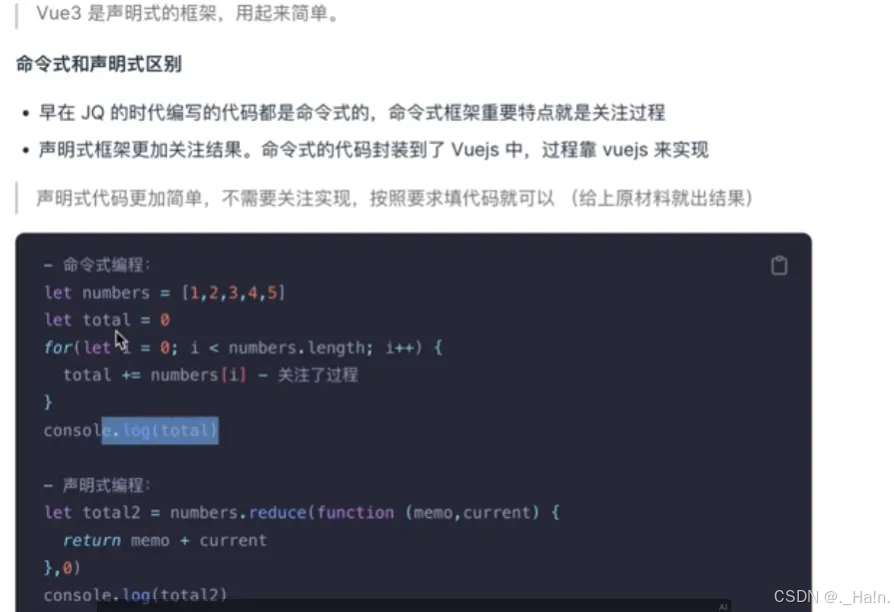
采用虚拟DOM
传统更新页面,拼接一个完整的字符串innerHTML 全量重新渲染,添加虚拟DOM后,可以比较新旧虚拟节点,找到变化在进行更新。虚拟DOM就是一个对象,用来描述真实DOM。
区分编译时和进行时
- 我们需要有一个虚拟DOM,调用渲染方法将虚拟DOM渲染成真实DOM(缺点就是虚拟DOM编写麻烦)。
- 专门写个编译时可以将模板编译成虚拟DOM(在构建的时候进行编译性能更高,不需要再运行的时候进行编译,而且vue3在编译中做了很多优化)
Vue3设计思想
- Vue3.0注重模块上的拆分,Vue3中的模块之间耦合度低,模块可以独立使用。
- 通过构建工具Tree - shaking机制实现按需引入,减少用户打包后体积。组合式API。
- Vue3允许自定义渲染器,扩展能力强,扩展更方便。
- 使用RFC来确保改动和设计都是经过Vuejs核心团队探讨并得到确认的。也让用户可以了解每一个功能采用或废弃的前因后果。采用RFC。
